How to Remove Background Noise from Mic?
 Mike Rule
Mike Rule
Updated on
Summary: Annoyed by mic background noise? Removing microphone background noise requires a combined approach—identify noise sources, use AI tools with proper model and filter settings, and optimize recording conditions with a quiet environment, high-quality mic, correct positioning, gain adjustment, pop filters, and acoustic treatment for clear, professional audio. This guide shows practical ways to reduce or remove it using better setup, equipment, and noise suppression software—for clear, professional audio on any platform.
Background noise is a common challenge when using microphones, whether you're recording a podcast, streaming, or attending virtual meetings. These unwanted sounds - such as static, ambient chatter, hiss, or hums - can significantly detract from audio quality.
Removing background noise enhances clarity, improves professionalism, and ensures a better experience for your audience. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to removing background noise from microphones, covering everything from basic setups to advanced tools and techniques.

Understanding Background Noise in Microphone
Background noise is any undesired sound captured by a microphone during recording or streaming that significantly impacts audio quality. One of the most common forms is environmental noise, which includes sounds like fans, air conditioning, traffic, or other ambient disturbances. These noises are usually constant and low-frequency, often resulting from external surroundings or a room's acoustics.
Another type of noise is electrical interference, often identified by a consistent hum or buzz. This occurs when microphones pick up interference from other electronic devices or poorly shielded cables. Ground loops, which arise from improper grounding of electrical systems, are a frequent culprit behind this issue.
Lastly, operational noise comes from the user's actions or the equipment itself. These include handling noise from moving the microphone, plosives from speech, or mechanical keyboard clicks during recording. Understanding these types of noise is essential for diagnosing and addressing the specific issues affecting audio quality.
How to Remove Background Noise from Microphone?
Achieving a noise-free microphone recording involves a combination of proper environment, equipment, and techniques. Each aspect plays a vital role in minimizing background interference.
Choose a Quiet Recording Environment
A quiet environment is the foundation of clean audio recording with a microphone. Selecting a space with minimal external noise sources can dramatically reduce background disturbances. Rooms with soft furnishings such as curtains, carpets, or cushions can help absorb sound and prevent echo. Additionally, turning off noisy appliances like fans or refrigerators before recording can make a significant difference.
Use a High-quality Microphone
Investing in high-quality equipment is another critical step. A dynamic microphone is often preferred for noise reduction as it captures sound directly in front of it while rejecting ambient noise. Similarly, directional microphones like cardioid or shotgun microphones focus on the speaker’s voice while minimizing peripheral sounds.
Position the Mic Correctly
Correct positioning of the microphone is equally important. Keeping the mic stable with a sturdy stand or boom arm reduces handling noise. Adjusting the microphone’s distance from the speaker’s mouth ensures that the voice is captured clearly while minimizing background pickup. To achieve the best sound quality while recording, it's recommended to stay as close to the microphone as you can.
Setup of Microphone Sensitivity and Gain
Properly setting up microphone’s sensitivity and gain levels is essential. High sensitivity and gain can amplify unwanted background noise, so these settings should be calibrated based on the recording environment. Most microphones and audio interfaces have controls to adjust these parameters, allowing for fine-tuned noise reduction.
Check Plugs
Checking connections is a simple yet effective way to eliminate potential noise sources. Loose or poorly connected plugs can introduce static or crackling sounds. Ensuring that the microphone input plug, audio source output plug, and power source plug are securely connected prevents such issues.
Use Pop Filters & Windscreens
Using a pop filter and windscreen helps tackle plosive sounds and wind noise. A pop filter, placed between the speaker and the microphone, blocks the impact of air caused by certain speech sounds. Windscreens, often used for outdoor recording, reduce wind interference effectively.
Use Acoustic Panels and Isolation Shields
Acoustic panels and isolation shields can further enhance the recording environment. Acoustic panels absorb sound waves and reduce echo, while isolation shields create a controlled recording space around the microphone. These tools are especially useful in rooms with poor acoustic properties.
Use Microphone Noise Suppression Software
Microphone noise reduction software offers an advanced solution for removing background noise. Programs like Audacity, Adobe Audition, and Winxvideo AI can isolate and remove unwanted sounds during or after recording. If you have recorded a video or audio with background noise, you can make use of such a tool.
Winxvideo AI is a fantastic option for anyone looking for user-friendly, AI-driven software to remove background noise in microphones. The latest version added a new Audio AI capability to allow users to eliminate background noise from your audio and video files with ease. Utilizing advanced AI technology, it effectively minimizes common distractions like traffic sounds, wind, microphone interference, and other background noise, ensuring you achieve outstanding sound quality.
 Free Download
Free Download
 Free Download
Free Download
Winxvideo AI is for PC, while Macxvideo AI (from our MacXDVD brand) is for macOS.
How to Reduce Background Noise on Mic Windows/Mac?
Like many other users, you may wonder how to eliminate background on mic on Windows 11/10 or Mac. Reducing background noise on Windows 11/10 and Mac involves built-in system settings and third-party applications. Both platforms provide users with effective tools to enhance audio clarity.
On Windows 11/10:
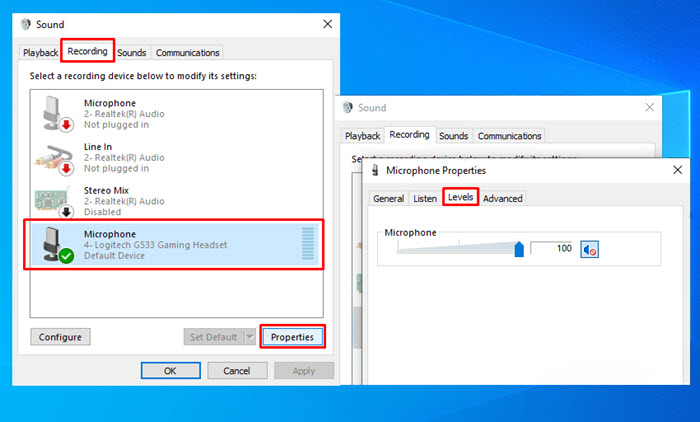
1. Navigate to "Hardware and Sound" from your computer’s control panel.
2. Select "Sound" and go to the recording section.
3. Right-click on the microphone bar and go to the "Properties" section.
4. You’ll see the "Levels" tab with the Microphone Boost tool.
5. To reduce background noise, move the dial on the microphone boost down completely.
6. Turn the microphone dial up completely.
7. Go to the "Enhancements" tabs and ensure that the "Acoustic echo cancellation" box and "Noise suppression" box are checked.
8. Then, the system automatically filters out background noise during real-time audio input.
On Mac:
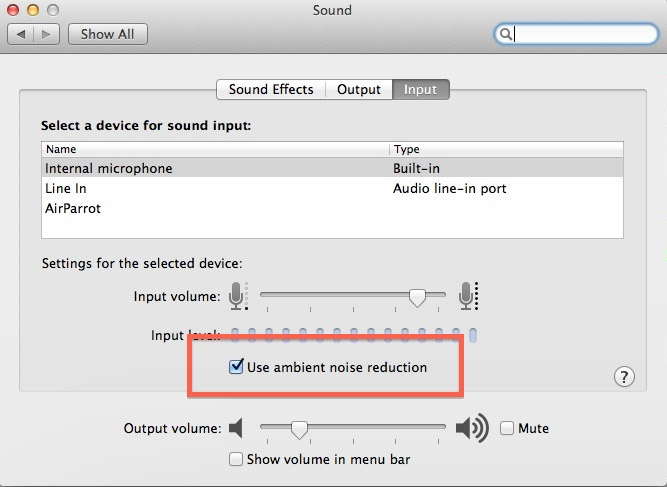
1. Open "System settings" and navigate to "Sound".
2. Under the "Output & Input" section, select "Input". You’ll see your Mac’s microphone, labeled "Built-in", and any external microphones.
3. Depending on your computer’s model, you will have a "Use ambient noise reduction" option. Note that not all models have a microphone offering this capability.
4. You can easily modify the "Input volume" for any microphone, including your built-in one, using the sliding bar. This allows you to control how much sound the microphone picks up. It’s a good idea to do a few test recordings to find the input volume that gives you the best audio clarity.
How to Remove Background Noise from Video/Audio?
As previously stated, an alternative method for eliminating background noise from a microphone involves utilizing microphone noise suppression software. Should your videos, audio tracks, podcasts, or similar content contain background noise, you may employ Winxvideo AI to effectively cancel out such noise and echoes, adjust voice volume levels, and make the audio studio-quality.
How to reduce mic background noise with Winxvideo AI?
Step 1. Download Winxvideo AI, install and launch it on your computer.
Step 2. On the main interface, click on the "Audio AI" button.

Step 3. Directly drag and drop the video or audio file that you want to remove the background noise. Or you can also click the "Add Media" button at the bottom to browse and select the file to import.
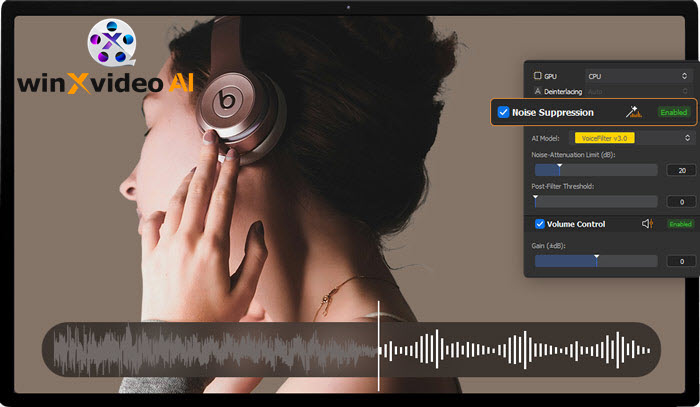
Step 4. Make sure the Noise Suppression is ticked on, choose the preferred AI model, and adjust the parameters accordingly.
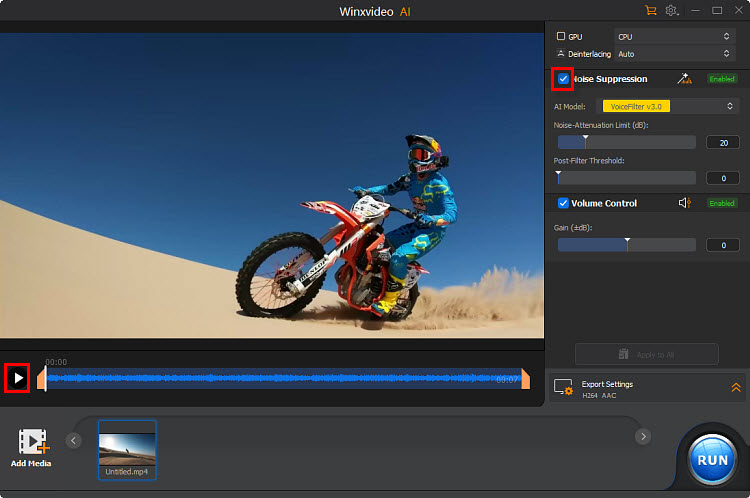
- AI Model: There are 2 AI models designed to help handle a variety of background noise.
- Noise Attenuation Limit (dB): It pertains to the highest degree of noise suppression measured in decibels (dB). This metric indicates the extent of noise elimination while preserving the integrity of the primary audio. A higher threshold effectively reduces more noise but may compromise audio quality, whereas a lower threshold allows for a more authentic sound experience. Striking a balance between these parameters is essential for achieving clarity in sound. It is advisable to configure the limit between 6-12 dB for minimal noise reduction and 18-24 dB for moderate noise suppression.
- Post-Filter Threshold: This parameter regulates the extent of additional noise elimination following the primary noise suppression procedure. It establishes a boundary for the removal of residual noise, thereby ensuring that the primary audio remains distinct while minimizing undesirable background sounds. A lower threshold (0.01-0.02) offers a gentler filtering effect, maintaining the natural sound quality in quieter settings, whereas a higher threshold (0.03-0.05) enforces more robust filtering, which is advantageous in environments with moderate noise, such as background hum or distant conversations.
- Volume Control: It enables users to adjust audio loudness by increasing or decreasing the signal.
Step 5. If you have multi-track audio, you can right-click on the chosen file, select the specific track you want to modify, and then follow the same process as before.
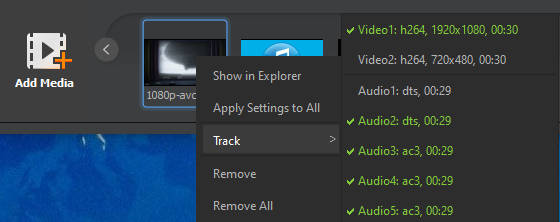
Step 6. Click on the "Play" button to preview the audio after noise removal.
Step 7. When everything is OK, hit the "RUN" button to export your audio with the background noise removed.
 Free Download
Free Download
 Free Download
Free Download
Winxvideo AI is for PC, while Macxvideo AI (from our MacXDVD brand) is for macOS.
Winxvideo AI can reduce types of background noise efficiently:
Environmental noise:
- Wind noise caused by air movement over the microphone or outdoor wind.
- Traffic noise from passing vehicles, horns, or engines.
- Ambient chatter from crowds or people talking at a distance.
- Birds and insects’ chirping or buzzing, or barking dogs, meowing cats, etc.
- Rain or thunder sounds.
- Water sounds like flowing rivers, dripping faucets, or crashing waves.
- Rustling leaves or hail.
Mechanical noise:
- Humming or whirring sounds from air conditioning or heating units.
- Background hum from refrigerators, washing machines, or microwaves.
- Noises from printers, keyboards, and photocopiers in workplace environments.
Electronic noise:
- Electrical hum: a low-frequency buzz caused by poor grounding or electrical interference.
- Static noise: white noise or crackling sounds from faulty cables or electronic interference.
- Feedback loops: a high-pitched squeal caused by a microphone picking up audio from nearby speakers.
- Digital artifacts: glitches or beeps resulting from compression or signal issues in digital recordings.
Room noise:
- Echo: reflection of sound waves off hard surfaces, creating a repeated effect.
- Reverberation caused by multiple reflections in a room.
- Footsteps or movement noise from people walking or objects being moved within the recording space.
- Creaking or squeaking from furniture or doors in the background.
Human-made noise:
- Breathing or sniffing.
- Keyboard clicks or mouse sounds.
- Clothing rustle: movement of fabric against the microphone.
- Unintentional speech sounds: coughing, throat clearing, or lip smacking.
- Handling noise from adjusting the microphone or camera.
- Cable rustling: movement of wires during recording.
- Explosive sounds from pronouncing plosive consonants (like "P" or "B").
By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can achieve professional-grade audio free from distracting background noise from microphone. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced audio enthusiast, these techniques will elevate your recordings to the next level.
Just Released: Vocal removal and instrumental separation are now in Winxvideo AI. Make karaoke or remixes faster than ever. If you are interested in removing vocals from YouTube, click here >>
 FAQs
FAQs
Stopping a mic from picking up background noise requires a combination of environmental adjustments, proper equipment, and optimized settings. Recording in a quiet space, using a noise-isolating microphone, and adjusting sensitivity levels are some practical steps. Additionally, software tools can help suppress unwanted noise during and after recording.
Background noise on a voice recording can be eliminated through post-processing with audio editing software. Tools like Audacity, Adobe Audition, or Winxvideo AI offer noise reduction features that isolate and remove specific sound frequencies. Using a directional microphone and ensuring optimal recording conditions also minimizes noise.
Yes, there are microphones specifically designed to cancel background noise. Dynamic microphones and directional microphones, such as cardioid or shotgun models, are excellent at rejecting unwanted ambient sounds. These microphones focus on capturing audio from a specific direction, making them ideal for noisy environments.
Background noise in a microphone can result from various factors, including environmental sounds, electrical interference, or improper settings. Common causes include high microphone sensitivity, loose connections, or inadequate acoustic treatment in the recording space.
Dynamic microphones are effective at reducing background noise due to their design. They capture sound directly in front of the mic while rejecting noise from other directions. This makes them suitable for noisy environments or live performances where ambient sounds are prevalent.
Testing a microphone for background noise can be done using recording software or online tools. By recording a short audio clip in the intended environment, you can identify any unwanted sounds. Adjusting settings like gain or sensitivity and experimenting with positioning can help isolate and address noise issues.